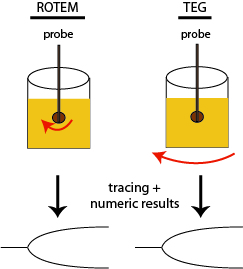
With viscoelastic clot detection, a probe is inserted into a cup containing the patient sample (usually whole blood). Then either the probe is rotated within the cup (thrombelastometry with the ROTEM) or the cup is rotated around a fixed probe (thrombelastography or TEG). Changes in the movement of the cup in relation to the probe results in a tracing that reflects the kinetics of fibrin formation (shown above) and fibrinolysis (not shown), with numerical measurements pertaining to these kinetics and the strength of the resulting fibrin clot.